Kolb's concept has been expanded upon by Honey and Mumford using more common terminology. According to Honey and Mumford, there are four distinct learning styles, each of which corresponds to a particular phase of the learning process. Activists, Reflectors, Theorist, and pragmatists are these (Australian government department of health and aged care, 2014).
Figure 01: Connection between Kolb’s Learning Cycle and Honey & Mumford’s Learning Styles
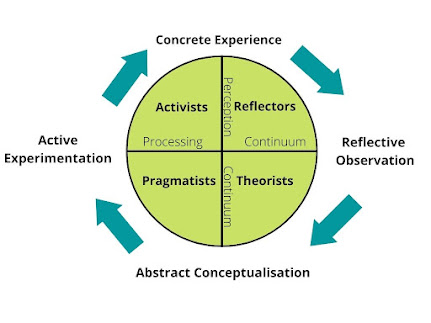
Kolb’s experiential cycle in Figure 01 have two continue the horizontal axis is the perception continuum which goes from “Active Experimentation” to “Reflective observation”. The vertical axis is the perception continuum, which goes from “Concrete Experience” to “Abstract Conceptualization”. The individual in between “Active Experimentation” and “Concrete Experience” are identified as Activists. If the Person places himself between “Concrete Experience” and “Reflective observation” he is recognized as a Reflector. The person falling in between “Reflective observation” and “Abstract Conceptualization” is termed a theorist and finally, individuals place themselves in between “Abstract Conceptualization and “Active Experimentation” recognized as Pragmatics (Richlin, 2006).
Let’s get
a better understanding of Honey and Mumford’s learning styles and their
practical applications using examples from the banking sector.
- Activists
People who
are enthusiastically engaged in new tasks and take on new experiences without
bias are recognized as Activists (Armstrong, 2014). They involve in new
experiments and perform high in emergencies. They solve problems instinctively
and they believe in doing things. Activists prefer to act on subjective
feelings when it comes to problem-solving. These individuals largely depend on
information from other people without creating their information by analysis
(Richlin, 2006). These sorts of learning styles suites more action-oriented job
roles like Marketing officers. These employees will be actively involved in
performing tasks and largely depend on the information provided to them by
other departments and superiors. These employees will have to make quick
decisions in unexpected situations. For example, convincing a demanding customer
for a sale will require the instinctive problem-solving capabilities of the
employee to provide compelling solutions then and there to create customer
satisfaction.
- Reflectors
Those who
step back and consider fresh encounters from many perspectives are considered
reflectors. They gather information, think about it, and conclude (Armstrong,
2014). They are excellent at creating ideas and seeing things from different
angles. Reflectors prefer situations that demand’ a wide range of ideas such as
brainstorming sessions with multicultural learning opportunities (Richlin,
2006). This type of learning style suites employees who are attached to
departments that perform investigative tasks like the inspection department.
These employees will require gathering information related to various incidents
and analyzing them to identify actual reasons. Upon concluding it will lead to
corrective measures.
- Theorists
People who develop logical theories
through adapting and applying their observations are identified as Theorists.
They frequently strive for perfection (Armstrong, 2014). Theorists stand out in
inductive reasoning and pay more attention to abstract concepts rather than
people. They are highly capable of creating theoretical models (Richlin, 2006).
This learning style is important to the top-level management of the
organization. When they perform their tasks they will have to make strategies
using theoretical models to find solutions to complex problems. An example is
the development of a strategy by top management to enhance the diminishing
deposit portfolio of the bank by adopting theoretical concepts of industrial
rivalry.
- Pragmatists
Individuals who are eager to test new concepts, methods, and ideas to determine if they work are recognized as pragmatists (Armstrong, 2014). Pragmatists use leanings to find solutions to actual problems. They favor technical tasks and excel in the practical application of concepts. This learning style is important to all employees who perform technical tasks (Richlin, 2006). As an example, a recruit attached to the account opening counter will perform duties practically applying the concepts, methods, and ideas he learned and developed in the introduction program. The recruit will determine the effectiveness of the leanings by practicing them in an actual working environment.
Referencing
Armstrong, M. &
Taylor, S. (2014) Armstrong’s handbook of
human resource management practice (13th ed). Kugan page
limited.(Online).Available at: https://www.academia.edu/32280546/ARMSTRONGS_HANDBOOK_OF_HUMAN_RESOURCE_MANAGEMENT_PRACTICE_i. Accessed on July 28, 2022
Australian government department of
health and aged care (2004) Identifying your personal learning style,
Resources. (Online). Available at: https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/publications/publishing.nsf/Content/drugtreat-pubs-front1-wk-toc~drugtreat-pubs-front1-wk-secb~drugtreat-pubs-front1-wk-secb-2~drugtreat-pubs-front1-wk-secb-2-5~drugtreat-pubs-front1-wk-secb-2-5-ide#:~:text=Honey%20and%20Mumford%20(1992)%20have,%2C%20Reflector%2C%20Theorist%20and%20Pragmatist. Accessed on August 21, 2022.
Richlin, L (2006) Blueprint for Learning: Constructing College Courses to Facilitate,
Assess, and Document Learning (1st ed). Stylus publishing LLC.
Sterling, Virginia. (online). Available at: https://books.google.lk/books?id=Xiu4ij6-et4C&pg=PA27&dq=kolb%27s+learning+cycle&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjm2NmqrLr5AhU5RmwGHf_XBCo4ChDoAXoECAsQAg#v=onepage&q=kolb's%20learning%20cycle&f=false. Accessed on August 13, 2022.



Although the LSQ was designed for use with management trainees, it has been used in a variety of settings, including education. However, concerns have been raised about the psychometric qualities of LSQ. Duff and Duffy (2002) report a failure to support the existence of the bipolar dimensions or learning styles proposed by Honey and Mumford and found that the LSQ has only modest levels of internal consistency (between 0.52 and 0.73 for the four style subscales). Given that their sample consisted of 388 undergraduate students, Duff and Duffy concluded that the LSQ is not an acceptable alternative to the LSI and that its use in higher education is premature.
ReplyDeleteReshan I firmly agree with you. There are arguments about the psychometric qualities of LSQ. But also, we can identify many ways that we can apply Kolb's learning cycle theory in practice to create a better learning experience for learners. According to Turesky and Gallagher (2011), Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory offers a framework that is especially helpful for coaching managers as they build the leadership abilities required to best manage complicated situations and the coaching relationship. To improve the coaching process, we contend that a successful coach can modify his or her learning style to fit with the client's desired learning style.
ReplyDelete